Beyond the Basics: Why Advanced Segmentation is Non-Negotiable
In a world saturated with digital noise, generic email blasts are destined for the spam folder. The key to capturing attention, fostering loyalty, and driving real revenue lies in speaking directly to your audience's unique needs and behaviours. This is where advanced email marketing segmentation comes into play. It's the strategic practice of dividing your email list into smaller, more focused groups based on specific criteria.
We're moving beyond simple first-name personalisation. We are talking about sophisticated strategies that consider everything from a subscriber's purchase history and engagement level to their lifecycle stage and location. To truly harness the power of personalised campaigns, it's essential to understand various customer segmentation techniques that form the foundation of effective marketing. By tailoring your messaging with this level of precision, you transform your emails from unsolicited interruptions into valuable, anticipated communications.
This guide will explore seven powerful email marketing segmentation examples, providing deep strategic analysis and actionable tactics you can implement immediately. We will break down the 'how' and 'why' behind each method, from demographic and behavioural splits to psychographic profiling. Our goal is to empower you to build a more intelligent, responsive, and profitable email marketing programme.
1. Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation is one of the most fundamental yet powerful email marketing segmentation examples. This strategy involves dividing your email list into subgroups based on observable, statistical characteristics of a population. These traits can include age, gender, income level, occupation, education, marital status, and geographic location. By grouping subscribers based on these shared attributes, you can create more personalized and relevant email campaigns that speak directly to their specific life circumstances and needs.

For instance, a real estate company can leverage this by sending emails about luxury high-rise apartments to high-income earners in urban centres, while targeting suburban families with listings for larger, family-friendly homes near good schools. This approach ensures the content is not just generic but highly applicable to the recipient's life stage and financial capacity, dramatically increasing engagement and conversion potential.
Strategic Analysis: The Sephora Example
Global beauty retailer Sephora masterfully employs demographic segmentation, particularly focusing on age. Instead of sending a one-size-fits-all newsletter, they tailor product recommendations and content to different age brackets.
- Younger Audience (18-25): This segment receives emails featuring trendy makeup, celebrity collaborations, and tutorials for achieving the latest looks seen on social media platforms like TikTok.
- Mature Audience (40+): This group gets content focused on high-performance skincare, anti-ageing products, and sophisticated, classic makeup looks. The messaging emphasizes product efficacy and long-term benefits rather than fleeting trends.
By doing this, Sephora acknowledges that a 20-year-old’s beauty concerns are vastly different from a 50-year-old’s. This targeted strategy makes each subscriber feel understood, fostering a stronger brand connection and driving sales for the most relevant products.
Actionable Takeaways
- Use Progressive Profiling: Don't overwhelm new subscribers with a long form. Start by collecting essential data like name and email. Later, use follow-up emails or preference centres to ask for their birthday (for age), location, or other relevant details in exchange for a special offer or personalized content.
- Combine Demographic Data: Enhance precision by layering demographic factors. For example, a campaign could target "women aged 25-35 living in Dubai with a high income level" for a luxury product launch.
- Respect Privacy: Be transparent about why you are collecting demographic data and comply with privacy regulations like GDPR. Assure subscribers their information is secure and will be used to improve their experience.
2. Behavioral Segmentation
As one of the most effective email marketing segmentation examples, behavioural segmentation goes beyond who your subscribers are and focuses on what they do. This strategy involves grouping subscribers based on their actions, interactions, and engagement patterns with your brand. These behaviours can include purchase history, website browsing activity, email opens and clicks, product usage, or content consumption. By tracking these real-time signals, you can move past assumptions and create highly relevant, automated campaigns that respond directly to individual customer actions.

For example, an e-commerce store can use this to send a targeted email with a special discount to a user who repeatedly views a specific product but doesn't purchase. Similarly, a software-as-a-service (SaaS) company can send tutorial videos to users who have activated a new feature but haven't used it yet. This proactive and personalised communication makes subscribers feel that their journey is understood, significantly boosting engagement and conversions.
Strategic Analysis: The Spotify Example
Spotify's annual "Wrapped" campaign is a masterclass in behavioural segmentation. It leverages a year's worth of user listening data to create a deeply personal and shareable experience. Instead of a generic end-of-year summary, Spotify provides each user with a unique story based on their individual listening habits.
- Data Utilisation: Spotify analyses which songs, artists, genres, and podcasts a user listened to most frequently. It even calculates more obscure data points like total listening minutes and the user's "oldest" and "newest" song discoveries.
- Personalised Content: This data is transformed into a vibrant, animated slideshow highlighting the user's unique musical journey. It creates a sense of identity and belonging, turning data into an emotional connection. The campaign is delivered via in-app notifications and a dedicated email driving users to their personalised results.
By transforming behavioural data into a celebratory event, Spotify creates immense brand loyalty and generates massive organic social media buzz. It’s a perfect demonstration of how tracking user behaviour can be used not just for sales, but for building a powerful community and reinforcing brand love.
Actionable Takeaways
- Start with Engagement Basics: Begin by segmenting based on simple email interactions. Create segments for your most engaged subscribers (e.g., opened or clicked in the last 30 days) and a re-engagement segment for those who have been inactive for 90 days.
- Implement Abandoned Cart Workflows: This is a crucial first step for any e-commerce business. Set up an automated email series that triggers when a user adds items to their cart but leaves your site without completing the purchase.
- Use RFM Analysis: Analyse Recency, Frequency, and Monetary value to identify your best customers. Reward these high-value segments with exclusive offers and early access to new products to foster loyalty and encourage repeat purchases.
- Track Key Website Actions: Use tracking pixels or integrations with your email platform to monitor key on-site behaviours, such as viewing a pricing page, downloading a white paper, or watching a product demo video. Use these actions to trigger relevant, nurturing email sequences.
3. Purchase History Segmentation
Purchase history segmentation is a highly effective method that groups subscribers based on their past transactional behaviour. This powerful strategy delves into data such as purchase frequency, average order value (AOV), products or categories purchased, and the time since their last transaction. By analysing these patterns, businesses can move beyond generic promotions and deliver hyper-relevant offers, product recommendations, and loyalty rewards that directly correspond to a customer's known preferences and buying habits.
For example, an e-commerce store like Zara can use this data to send style recommendations based on previously purchased fashion categories. A customer who frequently buys formal workwear would receive emails about new blazers and trousers, not the latest streetwear collection. This level of personalisation makes the marketing feel less like an advertisement and more like a helpful, curated shopping service, significantly boosting engagement and sales.
Strategic Analysis: The Starbucks Example
Starbucks has perfected purchase history segmentation through its integrated Rewards programme. The company meticulously tracks every transaction linked to a member's account, allowing it to build a detailed profile of each customer’s preferences and habits.
- Frequency-Based Offers: A customer who buys coffee every weekday morning might receive a "buy one, get one free" offer to encourage a weekend visit. Conversely, an infrequent visitor might get an email with bonus "Stars" on their next purchase to entice them back sooner.
- Product Preference Targeting: Starbucks knows if a customer prefers Frappuccinos over hot lattes or consistently adds a specific food item to their order. They use this to announce new related products or offer discounts on favourites, ensuring the message is always relevant. For instance, a regular oat milk latte drinker will be the first to know about a new oat milk-based beverage.
This data-driven approach allows Starbucks to create a deeply personalised experience that fosters loyalty, increases visit frequency, and maximises customer lifetime value. Each email feels like a custom offer designed just for the recipient.
Actionable Takeaways
- Create VIP Segments: Identify your top 5-10% of customers based on spending or frequency. Create an exclusive VIP segment for them, offering early access to sales, special discounts, or loyalty rewards to acknowledge their value and encourage continued patronage.
- Develop Win-Back Campaigns: Segment customers who haven't made a purchase in a specific timeframe (e.g., 60-90 days). Target this "lapsed" group with a special "We Miss You" offer or a survey to understand why they've been away, providing a clear incentive to return.
- Leverage Purchase Timing for Replenishment: For consumable products (like coffee, skincare, or vitamins), track the typical purchase cycle. Send automated reminder emails just before a customer is likely to run out, making reordering convenient and capturing the repeat sale.
4. Engagement Level Segmentation
Engagement level segmentation is a powerful method that involves categorising subscribers based on how they interact with your emails. This strategy analyses metrics like open rates, click-through rates, and conversion history to group users into tiers such as highly engaged, moderately engaged, and inactive. This is one of the most crucial email marketing segmentation examples because it allows you to protect your sender reputation, reduce unsubscribe rates, and deliver content that perfectly matches each subscriber's level of interest.
By identifying your most loyal fans, you can reward them with exclusive content, while a different approach can be used to re-engage those who have drifted away. This ensures your efforts are focused where they will have the most impact, preventing list fatigue and improving overall campaign performance. It's about sending the right message to the right person at the right frequency.
Strategic Analysis: The Grammarly Example
Grammarly, the AI-powered writing assistant, excels at using engagement-based segmentation to keep its massive user base active. Their strategy is a masterclass in recognising and acting on user behaviour signals.
- Active Users: Regularly engaged users receive value-packed emails, including weekly writing statistics, performance insights ("You were more productive than 85% of users"), and tips for using advanced features. This reinforces the product's value and encourages continued use.
- Inactive Users: When a user's activity drops, Grammarly's automation triggers a re-engagement campaign. These emails don't just say "we miss you"; they offer compelling reasons to return, such as highlighting new features, offering a discount on the Premium plan, or showcasing a powerful use case the subscriber may have missed.
This tiered approach allows Grammarly to maintain a healthy and highly active email list. They nurture their most active users to foster loyalty while systematically working to win back those at risk of churning, all through carefully timed and contextually relevant messaging.
Actionable Takeaways
- Define Clear Engagement Tiers: Establish specific criteria for each segment. For example, "Highly Engaged" could be those who opened or clicked in the last 30 days, while "Inactive" might be those with no opens in 90 days. Use these tiers to build distinct communication cadences.
- Create Automated Re-engagement Workflows: Don't wait until a subscriber is gone for good. Set up automated email sequences that trigger after a certain period of inactivity. You can find excellent blueprints and marketing automation workflow examples on grassrootscreativeagency.com to get started.
- Reward Your Best Subscribers: Treat your most engaged segment like VIPs. Give them early access to new products, exclusive discounts, or behind-the-scenes content. This makes them feel valued and transforms them into powerful brand advocates.
5. Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation categorises subscribers based on their physical location, such as country, region, city, or even post code. This location-based approach is a cornerstone of many successful email marketing segmentation examples, allowing brands to deliver region-specific content that feels incredibly personal and timely. By leveraging location data, marketers can promote local events, account for different time zones, acknowledge weather patterns, and respect cultural nuances, ensuring their message is always relevant to the subscriber's immediate environment.

For example, an outdoor retailer like REI can send promotions for insulated, waterproof jackets to subscribers in cold, rainy climates while simultaneously marketing lightweight hiking gear to those in warmer, drier regions. This targeted approach boosts engagement by providing a solution that is directly applicable to the recipient's daily life, making the brand feel more like a helpful local advisor than a distant corporation. This strategy is also vital for businesses looking to enhance their local digital presence, a key component of effective local SEO in Dubai and other major urban centres.
Strategic Analysis: The Starbucks Example
Starbucks is a global master of geographic segmentation, using it to drive foot traffic to its stores and create a sense of local community. Their email strategy goes far beyond generic national promotions, drilling down to city-specific and even store-specific offers.
- Weather-Based Promotions: Subscribers in cities experiencing a heatwave might receive an email promoting a discount on iced coffees and Frappuccinos. Conversely, those in a colder area would see offers for hot lattes or seasonal warm beverages.
- Local Events and Store Openings: When Starbucks opens a new store, it sends targeted emails to subscribers within a specific radius, often including an exclusive opening-day offer. They also tie promotions to local festivals or holidays, making their marketing feel integrated with the community's activities.
This granular approach makes each email feel like a personal invitation. By acknowledging the subscriber's local context, Starbucks transforms a global brand into a neighbourhood coffee shop, strengthening customer loyalty and driving in-store sales with remarkable efficiency.
Actionable Takeaways
- Use IP-Based Geolocation: Upon signup, use the subscriber’s IP address to automatically capture their approximate location (city or country). This provides an immediate basis for segmentation without requiring users to fill out extra fields.
- Schedule Sends by Time Zone: Never send a global email blast at a single time. Segment your list by time zone and schedule your campaigns to arrive at an optimal time (e.g., 10 AM local time) for each segment to maximise open rates.
- Leverage Local Holidays and Events: Go beyond major national holidays. Incorporate regional events, local festivals, or city-specific celebrations into your campaigns to create highly relevant and timely content that resonates with the local culture.
6. Lifecycle Stage Segmentation
Lifecycle stage segmentation is a sophisticated strategy that organises subscribers based on their position in the customer journey. This powerful email marketing segmentation example moves beyond simple demographics to consider where a person is in their relationship with your brand, from being a new lead to a loyal advocate. This allows you to deliver highly contextual messages that nurture them from one stage to the next, significantly improving conversion rates and customer lifetime value.
The core idea is to align your communication with the subscriber's current mindset. A new lead needs educational content to build trust, while a long-time customer might appreciate exclusive access or loyalty rewards. This approach ensures your emails are always relevant, helpful, and timely. For a deeper dive into guiding prospects, you can find excellent lead nurturing campaign examples on grassrootscreativeagency.com.
The following infographic illustrates the typical progression a contact makes through the primary lifecycle stages.
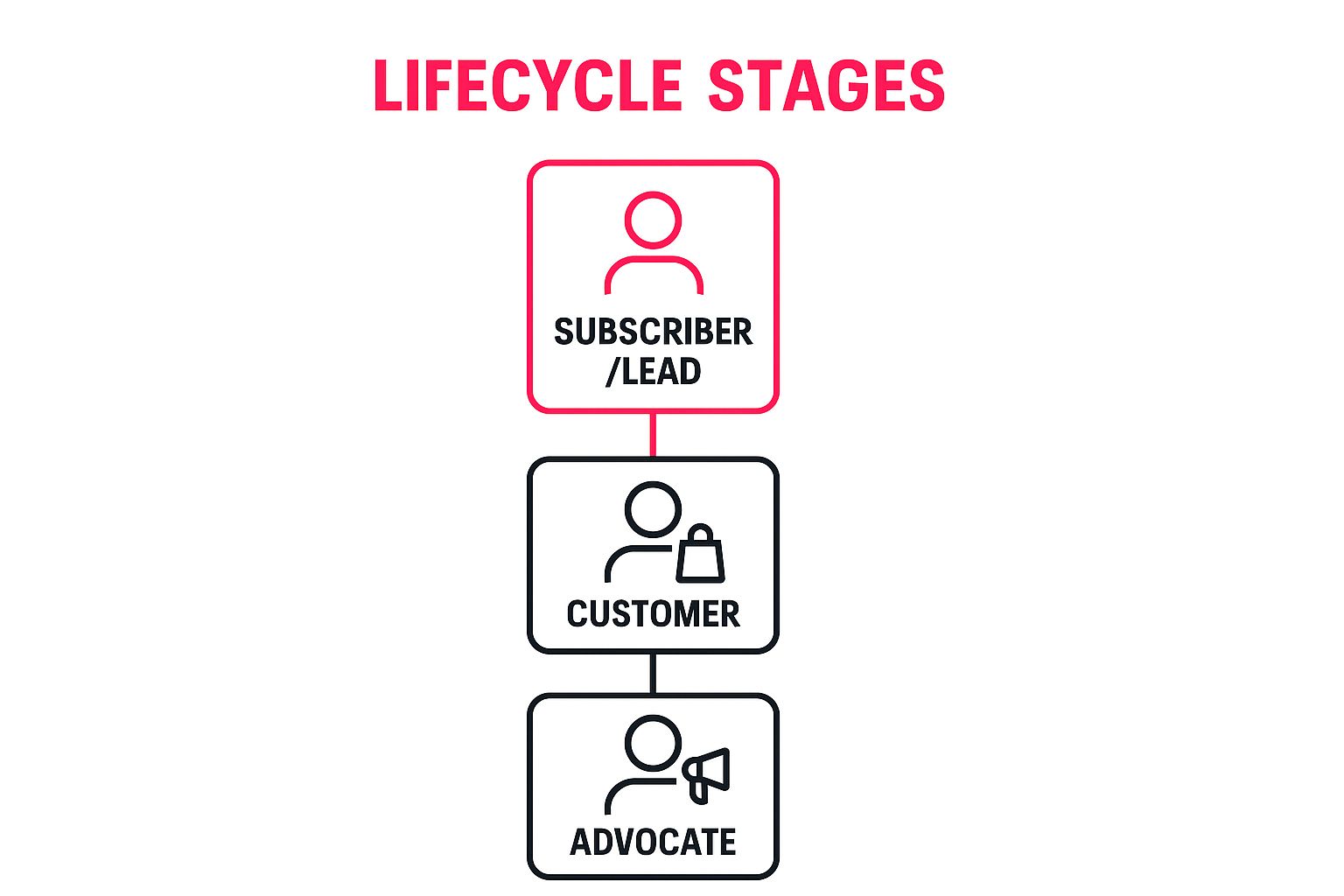
This hierarchy visualises the ideal journey, where your marketing and sales efforts successfully convert subscribers into paying customers, who then become enthusiastic brand advocates.
Strategic Analysis: The Slack Example
Collaboration platform Slack provides a masterclass in using lifecycle stage segmentation for user activation and conversion. Their email sequences are meticulously designed to guide users from a free trial to a paid subscription by focusing on behaviour and feature adoption.
- New Trial User (Lead): When a user signs up for a free trial, they enter an onboarding sequence. The initial emails are not about upgrading; they are about value. Slack sends tips on creating channels, inviting team members, and integrating apps, helping the user experience the platform's core benefits.
- Active Trial User (Marketing Qualified Lead): As the user and their team become more active, the messaging shifts. Slack will highlight advanced features that solve common collaboration problems, subtly demonstrating the limitations of the free plan and the power of the paid tiers.
- Near End-of-Trial (Sales Qualified Lead/Customer): In the final days of the trial, the emails become more direct, summarising the value the team has received (e.g., "You've sent 10,000 messages!") and clearly outlining the benefits of upgrading to a paid plan to retain their history and unlock more features.
This staged approach makes the upgrade feel like a natural and necessary next step rather than a premature sales pitch, effectively converting free users into paying customers.
Actionable Takeaways
- Define Your Stages: Clearly map out what each lifecycle stage means for your business (e.g., Lead, Marketing Qualified Lead, Customer, Advocate). Define the specific criteria or actions that move a contact from one stage to the next.
- Automate Stage Progression: Use your marketing automation platform to create workflows that automatically update a contact's lifecycle stage based on triggers like website activity, content downloads, or purchase history.
- Align Content with Stage: Create distinct email content for each stage. A "Lead" might get a blog post, a "Marketing Qualified Lead" a case study or webinar invitation, and a "Customer" a survey or a request for a review.
7. Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation is a sophisticated strategy that moves beyond 'who' your customers are to understand 'why' they make decisions. This powerful email marketing segmentation example involves grouping subscribers based on their psychological attributes, such as values, attitudes, interests, and lifestyle. By understanding these intrinsic motivators, you can craft email campaigns that create a deeper, more emotional connection and resonate with your audience on a personal level.
For example, a travel company could use psychographics to differentiate between subscribers who seek adventure and thrill versus those who prefer relaxing, luxurious getaways. The adventure-seeker would receive emails about mountain trekking in Nepal, while the relaxation-seeker would get offers for all-inclusive spa resorts in the Maldives. This ensures the messaging aligns directly with the subscriber's core desires, making it far more compelling than a generic travel offer.
Strategic Analysis: The Patagonia Example
Outdoor apparel brand Patagonia is a master of psychographic segmentation, building its entire brand identity around a specific set of values. They target consumers who are not just outdoor enthusiasts but are also deeply committed to environmentalism and sustainability.
- Value-Driven Content: Patagonia's emails often focus less on the products themselves and more on environmental activism, corporate responsibility, and stories of conservation. Their famous "Don't Buy This Jacket" campaign was a prime example, appealing directly to the anti-consumerist values of their core audience.
- Lifestyle Alignment: The content showcases a lifestyle of rugged adventure, minimalism, and a profound respect for nature. This reinforces the idea that buying from Patagonia is not just a purchase; it's a statement of personal values and an investment in a shared cause.
By focusing on these shared beliefs, Patagonia cultivates an intensely loyal community. Their subscribers feel like part of a movement, not just customers on an email list. This value-driven connection drives both brand loyalty and sales, proving that understanding a subscriber's worldview can be more powerful than knowing their age or location.
Actionable Takeaways
- Utilise Surveys and Quizzes: Directly ask subscribers about their interests, hobbies, and values. Use engaging quizzes like "What's Your Adventure Style?" to gather psychographic data in a fun, interactive way that provides immediate value to the user.
- Analyse On-Site Behaviour: Track which blog categories a subscriber reads or which product types they browse. Someone who frequently reads about sustainability is likely value-driven, while someone browsing high-performance gear is likely achievement-oriented.
- Create Value-Based Personas: Develop detailed buyer personas that include psychographic traits. Go beyond demographics to define their motivations, goals, and core beliefs. Use these personas to guide your email messaging and content creation.
7 Examples of Email Segmentation Methods Comparison
| Segmentation Type | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic Segmentation | Low – simple setup and data collection | Low – basic data easily collected via signup forms | Broad audience targeting, localized messaging | Product recommendations, timing optimization | Easy to implement, clear targeting, data widely available |
| Behavioral Segmentation | High – requires robust tracking and maintenance | High – analytics integration, ongoing data management | Highly personalized, improved conversion rates | Automated triggers, behavioral campaigns | Based on actual user behavior, strong ROI measurement |
| Purchase History Segmentation | Medium – requires integrated e-commerce systems | Medium – transactional data analysis required | Precise product recommendations, customer value identification | Loyalty programs, repeat purchase campaigns | Direct revenue correlation, identifies high-value customers |
| Engagement Level Segmentation | Medium – consistent monitoring needed | Medium – email interaction data and scoring | Optimized send frequency, improved deliverability | List health management, re-engagement campaigns | Reduces unsubscribes, maximizes active user engagement |
| Geographic Segmentation | Low to Medium – needs accurate location data | Low to Medium – location and time zone detection | Region-specific content, local compliance | Local promotions, weather-triggered campaigns | Highly relevant local targeting, supports compliance |
| Lifecycle Stage Segmentation | High – complex definitions and tracking | High – requires funnel tracking and automation | Improved conversion through funnel, customer journey alignment | Lead nurturing, customer onboarding, retention | Highly relevant messaging per stage, boosts lifetime value |
| Psychographic Segmentation | High – difficult data collection and analysis | High – surveys, social media analysis, persona building | Deep emotional connection, strong brand loyalty | Lifestyle marketing, value-driven campaigns | Creates emotional resonance, differentiates from competitors |
Putting Segmentation into Action: Your Strategic Blueprint
We've explored a powerful array of email marketing segmentation examples, from the foundational demographic and geographic data to the more nuanced behavioural and psychographic insights. The journey from generic email blasts to hyper-personalised conversations may seem complex, but it's a strategic imperative for any business aiming to thrive in a crowded digital landscape. The core principle is clear: relevance drives results. When you speak directly to a subscriber's needs, interests, and position in their customer journey, you don't just sell a product; you build a relationship founded on understanding and value.
The true mastery of email segmentation isn't about implementing all seven strategies at once. Instead, it’s about a deliberate, iterative process of testing, learning, and refining. Your strategic blueprint should be built on a foundation of your specific business goals and the data you can realistically collect and analyse.
Your Actionable Next Steps
To move from theory to implementation, focus on these key actions:
-
Start with a Foundational Blend: Begin by combining two powerful segmentation types. A great starting point for many businesses is merging behavioural data (like website pages visited or content downloaded) with demographic data (like job title or company size for B2B). This creates a robust initial segment that is far more effective than targeting based on a single attribute.
-
Define Your Goals for Each Segment: Don't create segments just for the sake of it. For a segment of "inactive subscribers," your goal is re-engagement. For a "VIP customer" segment, the goal is loyalty and advocacy. Aligning your messaging with a clear objective is critical for measuring success.
-
Leverage Automation for Scalability: Once you've defined your segments and goals, automation becomes your most valuable ally. A core component of putting segmentation into action involves implementing automated lead nurturing strategies, where personalised messages are delivered based on segment-specific behaviours. This ensures timely, relevant communication without manual intervention, which is especially crucial for converting new leads and re-engaging past customers.
The Long-Term Vision: A Dynamic Approach
Think of your segmentation strategy not as a static set of rules but as a living system. As you gather more data and customer feedback, your segments will evolve. What starts as a simple "purchase history" segment can later be layered with lifecycle stage data to differentiate between a first-time buyer and a loyal, repeat customer. This dynamic process, fuelled by continuous analysis, is what separates basic email marketing from a high-performing revenue channel.
The power of these email marketing segmentation examples lies in their adaptability. Whether you are a startup in the UAE or an established global e-commerce brand, the principles remain the same. Start small, prioritise your most valuable customer groups, and build complexity over time. The ultimate reward is a highly engaged audience that not only anticipates your emails but also acts on them, driving sustainable growth for your business.
Ready to transform your email marketing from generic sends to revenue-driving conversations? At Grassroots Creative Agency, we specialise in crafting data-driven email campaigns that leverage precise segmentation to deliver measurable results in the UAE and beyond. Let's build a strategy that connects with your audience and grows your brand.








